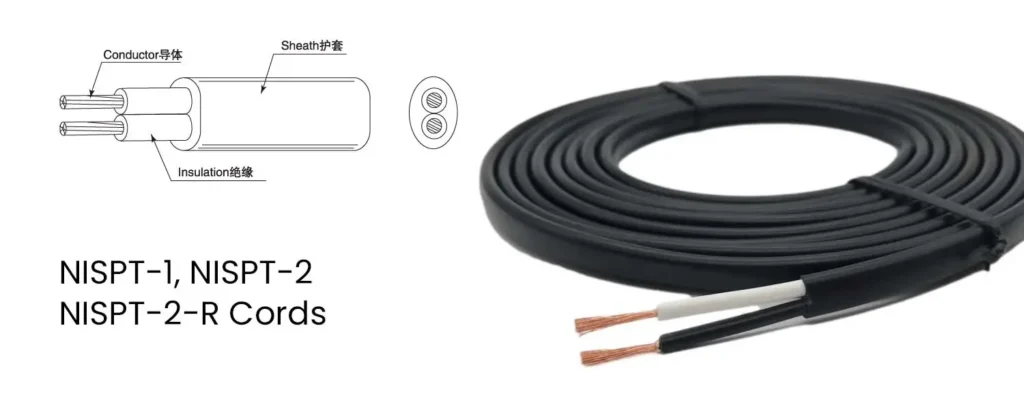
NISPT: This abbreviation stands for North American Service Parallel Thermoplastic and represents a type of service cord commonly used in low-power applications within dry environments. They share similar characteristics to the previously discussed SPT cords but cater specifically to the North American market. Here’s a breakdown of the available variations: NISPT-1: This type features two […]
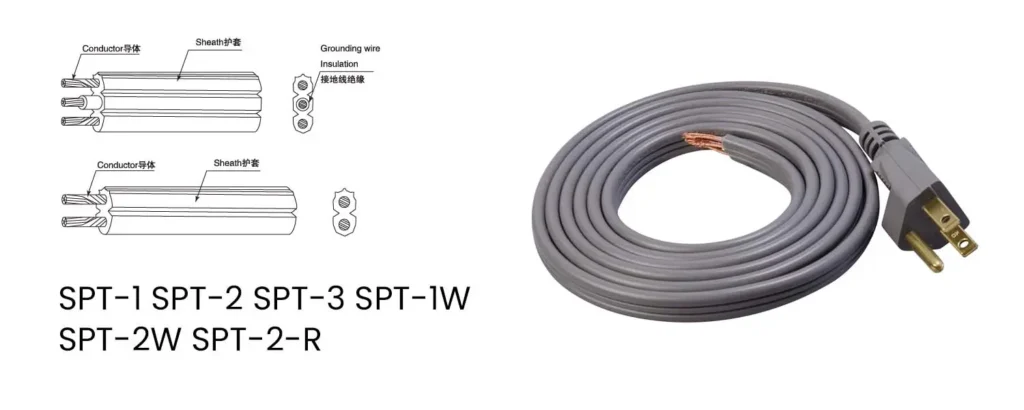
SPT (Service Parallel Thermoplastic) cords. They are primarily used for low-power applications within dry environments, such as: Lamps and lighting fixtures Christmas lights Small appliances (fans, radios) Extension cords (limited to specific lengths) Here’s a breakdown of their key differences: Code Description SPT-1 Two parallel conductors with a thin thermoplastic insulation layer. SPT-2 Two parallel conductors with […]
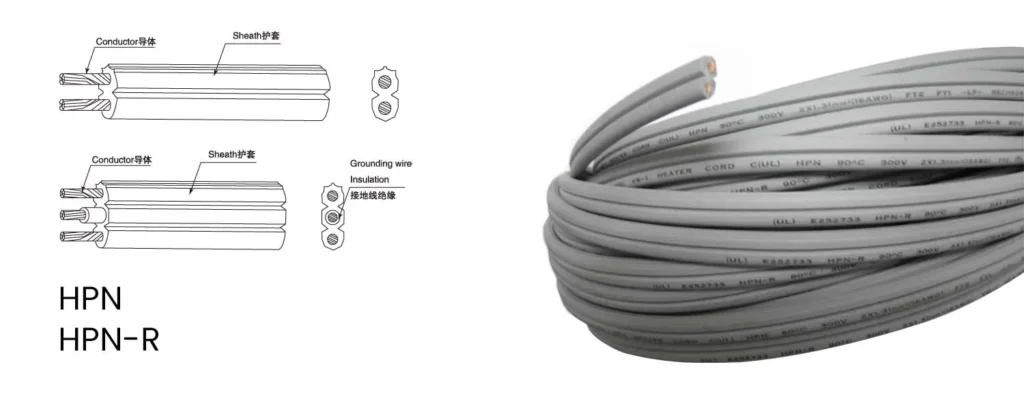
HPN (Heater Parallel Neoprene): Application: These cables are specifically designed for heater-type appliances like irons, toasters, and hot plates. Features: Parallel conductors: Conductors run side-by-side, allowing for higher current carrying capacity. Neoprene insulation: Offers superior heat resistance compared to standard thermoplastic insulation used in other cords. This is crucial for withstanding the high temperatures generated […]
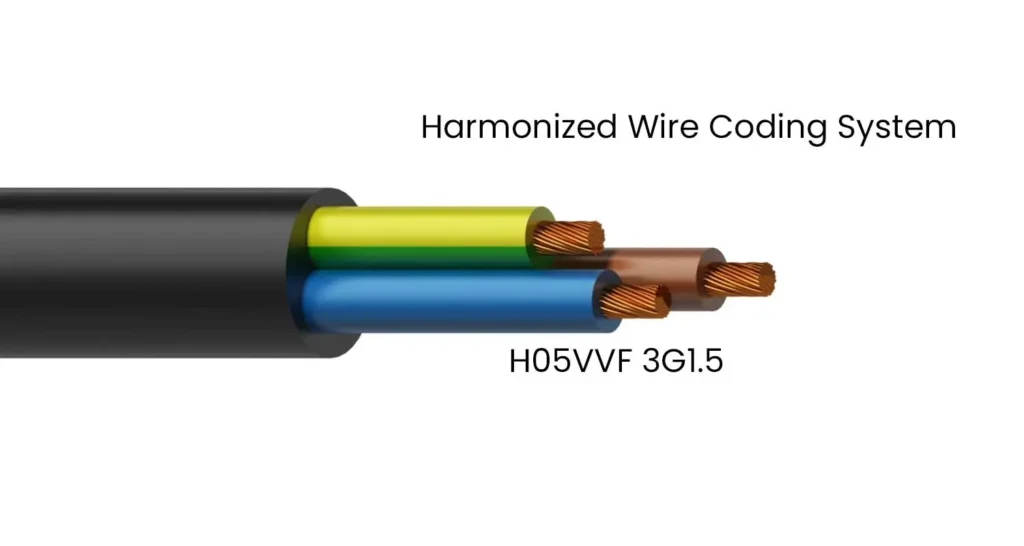
The Harmonized Wire Coding System standardizes the way electrical cables are marked and classified. This system, established by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), utilizes a series of letters and numbers to convey crucial information about the cable’s construction, properties, and intended use. Here’s a breakdown of the key components of the system: 1. First Letter: […]
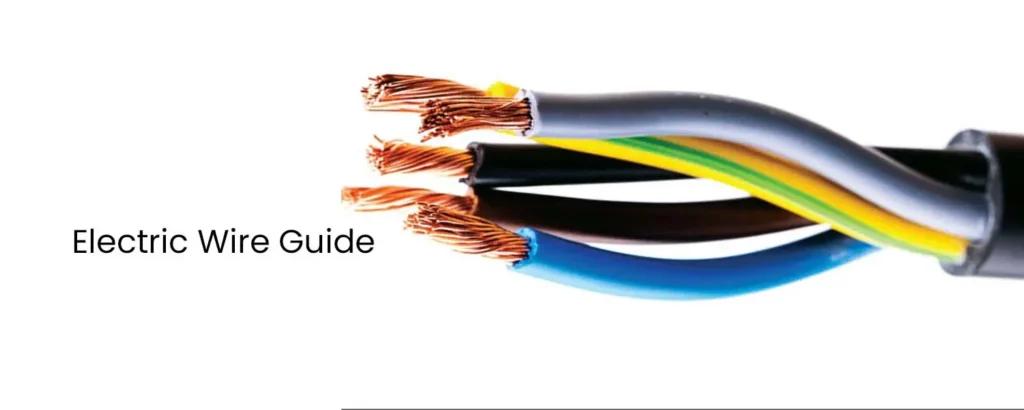
Electrical wires are the backbone of any electrical system, responsible for transmitting electricity safely throughout homes, buildings, and various appliances. Understanding the different types of wires is crucial for selecting the right one for your specific needs and ensuring a safe and efficient electrical installation. Key Wire Components Before delving into the types of wires, […]
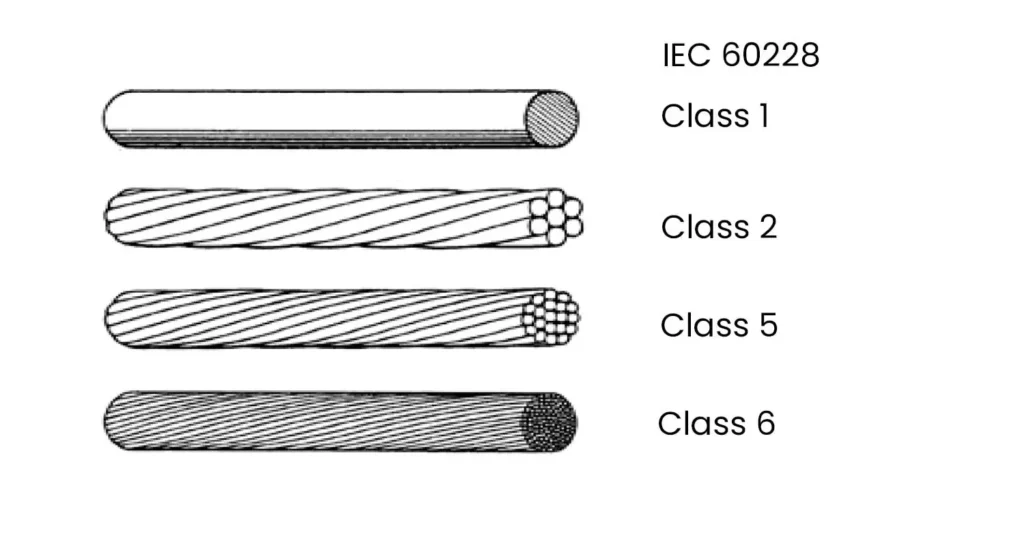
What is IEC 60228? The IEC 60228 is an international standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) that defines a set of standard wire cross-sectional areas for insulated cables. Key Points: Current Version: Third Edition published in November 2004. Purpose: Standardize wire sizes for consistent electrical performance. Focus: Defines cross-sectional areas instead of diameters. Benefits: Simplifies wire selection based […]
The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system, established in 1857, is a standardized method for measuring the diameters of round, solid, non-ferrous electrical wires used primarily in North America. Key characteristics of AWG: Logarithmic System: Increasing gauge numbers signify decreasing wire diameters, similar to other non-metric gauges. Distinct from Metric System: AWG differs from IEC 60228, […]
Introduced in: Brazil (2001) and South Africa (2013) to unify the plug and socket system. Features: Unique design:Triangular shape with two round prongs and a grounding pin. Safety features:Insulated sleeves on prongs to prevent accidental contact when partially inserted. Variants: Brazil: 10 amp and 20 amp versions with different pin diameters (4mm & 4.8mm). South […]
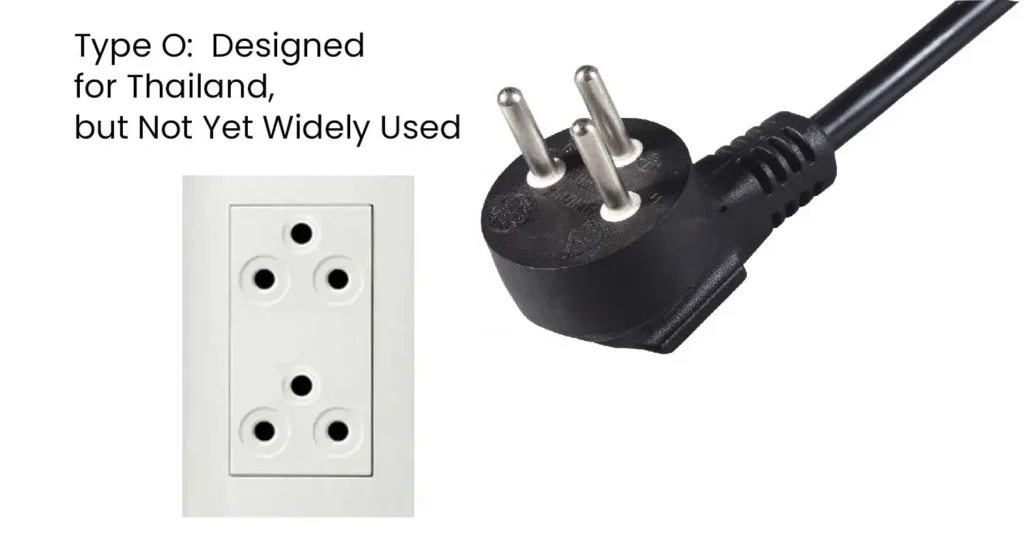
Used in: Thailand exclusively. Features: Rated for 16 amps. Three round prongs: Two power pins (19 mm, insulated) and one grounding pin (21.4 mm). Compatible with: Existing hybrid sockets (types A, B, C, and O). Future plan: Phase out compatibility with American types A and B plugs. Incompatible with: Type H (Israel), type K (Denmark), type E/F […]
Main usage: South Africa, Swaziland, and Lesotho. Features: Resembles type D but larger: Three round prongs in a triangle with larger size compared to the Indian type D. Grounded, 16 amp capacity. Pin details: Central earth pin: 28.6 mm long, 8.7 mm diameter. Line and neutral pins: 7.1 mm diameter, 18.6 mm long, 25.4 mm center-to-center […]