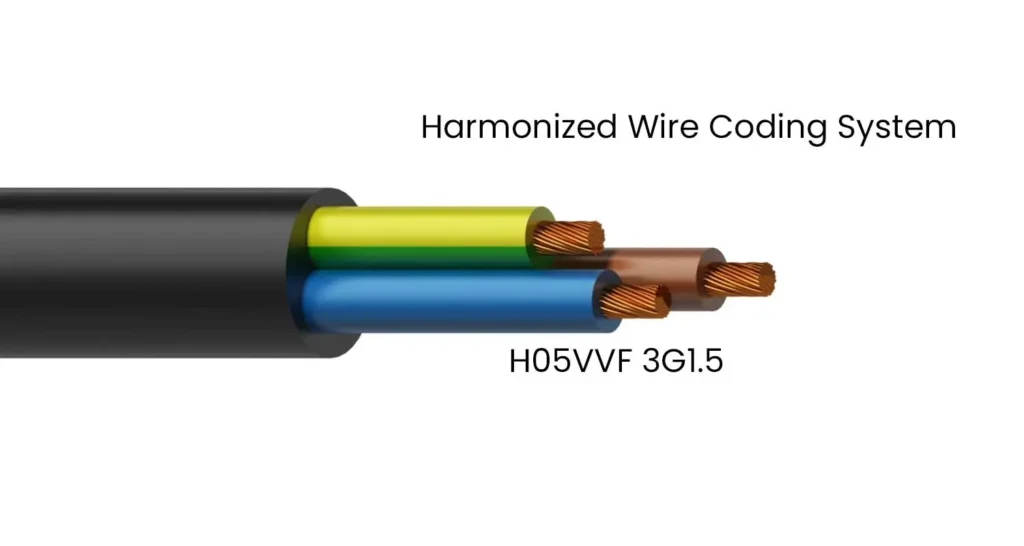
The Harmonized Wire Coding System standardizes the way electrical cables are marked and classified. This system, established by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), utilizes a series of letters and numbers to convey crucial information about the cable’s construction, properties, and intended use.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components of the system:
1. First Letter:
- H: Denotes a harmonized cable, adhering to IEC standards.
2. Second Letter:
- V: Indicates a PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) insulation material, the most common type.
- Other possibilities include:
- E: Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR)
- G: Rubber
3. Third Letter (Optional):
- F: Indicates flat conductors.
4. Fourth Letter (Optional):
- A: Denotes an armored cable with additional protection.
5. Numbers:
- These represent the number of conductors and their cross-sectional area in square millimeters (mm²).
- For example, “3G1.5” indicates a cable with three conductors, each with a cross-sectional area of 1.5 mm².
6. Additional Letters (Optional):
- Y: Indicates a harmonized control cable.
- C: Indicates a harmonized flexible cord.
- X: Denotes a special cable not covered by the standard.
Benefits of the Harmonized Wire Coding System:
- Standardization: Ensures consistent and clear communication of cable properties across different countries and manufacturers.
- Safety: Helps identify the appropriate cable for specific applications, reducing the risk of using incorrect cables that could lead to safety hazards.
- Ease of Use: Provides a straightforward way to understand cable characteristics without extensive technical knowledge.
Examples:
- H05VVF 3G1.5: This is a common type of power cable with three PVC-insulated conductors, each with a cross-sectional area of 1.5 mm². It’s suitable for general-purpose applications in dry environments.
- H07RN-F 3G2.5: This cable features three flat, rubber-insulated conductors with a cross-sectional area of 2.5 mm² and is designed for outdoor use due to its weatherproof properties.